Switching :
Two different switching techniques are used by the network :
- circuit switching
- packet switching.
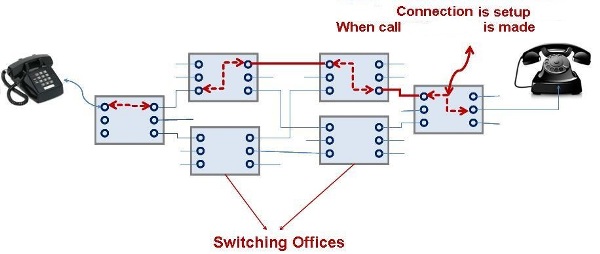
1. Circuit Switching:
- It is made of a set of switches connected by physical links in which each link is divided in n-channels.
- Circuit Switching takes place at Physical layer .
- The resources needed to reserved during the setup phase and remain dedicated for the entire duration of data transfer until the data transmission complete.
- There is no addressing involved during data transfer.
- Ex- Telephone lines.
Circuit Switching
2. Packet Switching :
- In packet switching data split into small units called packets.
- each packet is containing a header information and data.
Packet switching is further two types:
- Datagram Packet Switching
- Virtual Circuit Packet Switching
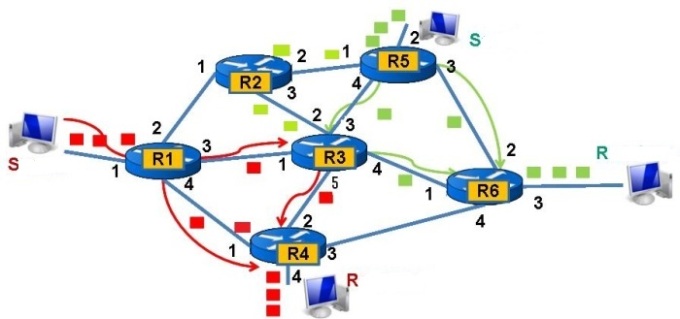
1. Datagram Packet Switching :
- In a datagram network each packet is treated independently of others.
- It is connection-less switching.
- Destination address is unchanged at each intermediate device.
- The delay between packets is not uniform.
- Packets may arrived at receiver out of order.
- Store and forward type of technique.
- Datagram switching is normally done at Network Layer
- IP uses Datagram based packet switching.
Datagram Packet Switching
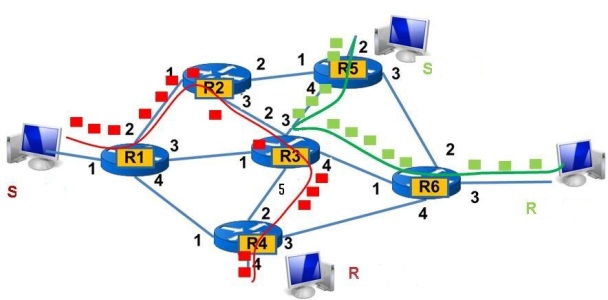
2. Virtual Circuit Packet Switching(VC) :
- VC switching is connection-oriented packet switching.
- A logical connection is establish between sender and receiver before data transfer starts.
- Connection established using signalling protocol.
- Signaling protocol first identify end to end path between sender and receiver.once a path is identified all packets follow the same path.
- This path is not reserved for this session alone multiple session can share the links in same path.
- After identify packet switches allocate VC IDs or label to uniquely identify each connection.
- The labels only have local significance at each intermediate switch, not having end-end significance.
- Packets are switched using these labels.
- At each intermediate device look at incoming label and link, based on this identify suitable outgoing link and label by consulting to a local virtual circuit table.
- After completion of data transfer labels are drooped from VC table.
- It is implemented at the Data link layer.
- VC based switching is very useful in switched WAN for fast switching.
- Ex- X.25,Frame-Relay, ATM and MPLS .
Virtual Circuit Packet Switching